Does Everyone Have Wisdom Teeth?
Many of us expect wisdom teeth in our late teens or early 20s. Did you realise not everyone gets this? Some people never grow wisdom teeth, even though one to four are common. Wisdom teeth, the third pair of molars, are in the back of your mouth. That’s why understanding when they generally appear and what difficulties they may create is important. The number of wisdom teeth varies among people; some may have four, some two, and some none at all.
Why Some People Never Develop Wisdom Teeth
A dental X-ray can detect wisdom teeth (3rd molars). Not developing these teeth might look odd, yet it is normal for some people.
The Dental Research Journal estimates that 5% to 37% of patients lack wisdom teeth, meaning they have no wisdom teeth at all. The reason is unknown, however genetics are important. If your parents did not have wisdom teeth, you may not either.
Environmental factors, food, and jaw function may also cause missing wisdom teeth. Wisdom teeth may not be visible, but they still exist. Impacted wisdom teeth remain beneath the gums. To avoid infections and pain, your dentist may prescribe removal.
When Do Wisdom Teeth Usually Erupt?
Wisdom teeth usually appear between the wisdom teeth age range of 17 and 21, but timing varies. Wisdom teeth may emerge earlier or later in life.
If your dentist recommends wisdom tooth removal, it is easier while you are younger. Extraction is easier at this age since your gums have softer bones and your nerve roots have not fully grown. Waiting until you are older may make removal harder and more painful due to bone hardness and fully formed nerve roots.
What Purpose Do Wisdom Teeth Serve?
Wisdom teeth removal is one of the most popular dental treatments since the mouth rarely has room for 32 teeth, especially if all four come in. It may be essential to remove them due to congestion.
Given that the mouth generally holds 28 teeth, you may ask what wisdom teeth do. One theory is that they replaced teeth for our ancestors who ate harder foods. However, modern people consume softer, easier-to-chew food and practise good dental care, decreasing the need for more teeth.
Our ancestors ate hard-to-chew meals, which could have caused tooth decay or gum disease without advanced dental care. Wisdom teeth could have more chewing surfaces for food processing. However, nowadays, wisdom teeth typically cause more harm than good. The wisdom teeth size is often large enough to cause crowding, which is why many people have them extracted.
Third Molar Agenesis vs. Impacted Wisdom Teeth: What’s the Difference?
It is important to know the difference between having no third molar agenesis and having wisdom teeth that are impacted. Though related to wisdom teeth, they reflect different disorders.
Third molar agenesis means not having wisdom teeth. People with this disorder do not grow wisdom teeth, often owing to genetics. However, impacted wisdom teeth cannot fully erupt. Lack of jaw space traps them beneath the gumline or partially visible.
On the other hand, impacted wisdom teeth can cause severe discomfort and gum infections. A dentist can monitor impacted teeth if they do not create any visible concerns. According to a Harvard University survey of 49 research involving over 83,000 people, no wisdom teeth percent is around 5–37%, showing that many people naturally never develop them.
Are There Any Problems Linked to Wisdom Teeth?
Wisdom teeth are natural, but if they do not grow properly or there is not enough room, they might cause problems. Some remove their wisdom teeth early to avoid future difficulties, while others wait until symptoms appear.
Problems with wisdom teeth include:
- Tooth Pain: Primarily experienced in the back of the mouth. Starting from the back of your mouth gums, the discomfort may be minor and intermittent. The pain can go away after a few days, but it may worsen, especially if chewing or biting is difficult.
- Swelling and Redness: Indications of wisdom teeth emergence or infection include painful swelling. A lot of people get redness or swelling around their gums, which can be painful.
- Impacted Teeth: Wisdom teeth may not develop properly due to insufficient jaw space. The gumline may trap these teeth, producing pain and pushing on surrounding teeth. This can cause jaw infection or pressure.
- Oral Infections: Since wisdom teeth grow in the rear of the mouth, they can trap food and germs in the gums, leading to oral infections. Pain, redness, swelling, unpleasant taste, and bad breath are symptoms.
- Cavities: Partial erupted wisdom teeth are more prone to cavities due to difficulty in cleaning the surrounding area. If food becomes caught around teeth, this might cause rotting.
- Shifting Teeth: Wisdom teeth may move or misalign if there is insufficient space when they push on surrounding teeth.
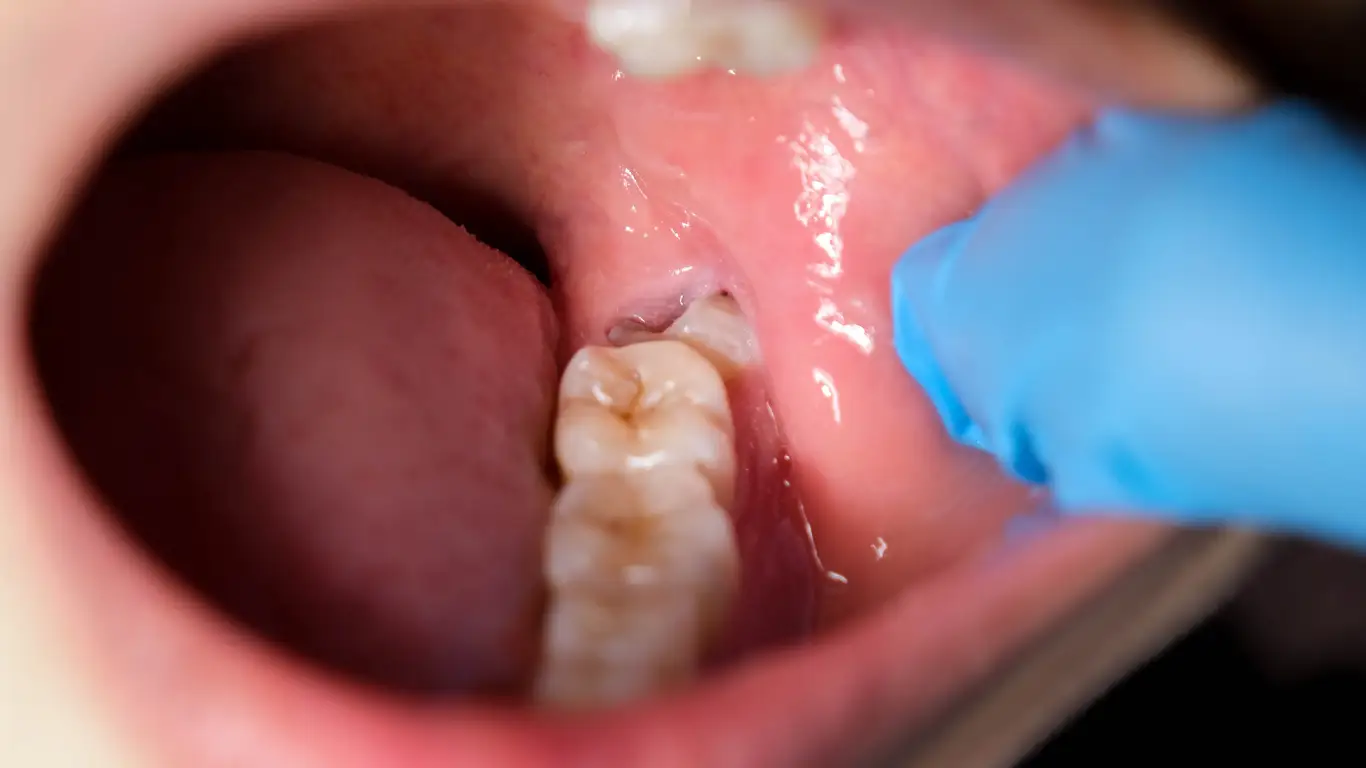
Do Wisdom Teeth Always Need to Be Removed?
You may wonder if those with wisdom teeth should automatically have surgery if you do not have any. Traditional wisdom teeth removal was popular even if they were not creating problems. A review of research by Cochrane Oral Health found no evidence to recommend routinely removing asymptomatic wisdom teeth.
Do everyone have wisdom teeth? Not necessarily. If you have them, your dentist and you should decide whether to remove them based on your mouth’s health and needs. If you are unsure about your wisdom teeth, talk to your dentist. Their counsel can help you make the greatest oral health decision. If removal is necessary, follow your dentist’s advice about safe foods after wisdom teeth removal to help with smooth recovery.
When Should You See a Dentist About Your Wisdom Teeth?
You should see your doctor if you have tooth pain or if you see your wisdom teeth starting to come in. X-rays can help your dentist figure out how many wisdom teeth you have and see if any problems are happening.
If you are in pain or having other problems, your dentist may suggest removal to keep things from getting worse. Here are some of the risks that having wisdom teeth can bring:
- Infections
- Bone loss
- Nerve pain
- Cavities
- Shifting teeth
If your wisdom teeth are not bothering you right now, your dentist may decide to monitor them and suggest removal in the future. Keep in mind, though, that extractions tend to get harder as you get older, so if you are having trouble, you should get help immediately. You can even consult a dentist in Turkey if you are considering affordable and professional dental care abroad.
The Bottom Line on Wisdom Teeth and Oral Health
Not everyone has wisdom teeth, and if you are lucky enough not to have them, you may not need to remove them. People who do have wisdom teeth should keep going to the dentist every six months as long as they are not causing any problems.
Your dentist can monitor how your wisdom teeth are growing and see if there are any problems. If they do, they can suggest that you remove them to protect your oral health. Understanding the truth about wisdom teeth helps you make informed decisions about whether to keep or remove them.














